Soal 6
Bacalah teks berikut dengan seksama, kemudian jawablah pertanyaan yang ada di bawahnya.
Text 6
How Does a Refrigerator Work?
A refrigerator is a device that uses a cycle of evaporation and condensation to transfer heat from the inside of the refrigerator to the outside, thus creating a cool environment for storing food. The main components of a refrigerator are a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve, and an evaporator.
The compressor is a pump that compresses a refrigerant, which is a fluid that can easily change its state from gas to liquid and vice versa. The refrigerant is usually a synthetic compound such as Freon. The compression of the refrigerant increases its pressure and temperature, turning it into a hot gas.
The condenser is a coil of metal tubes that is located at the back or the bottom of the refrigerator. The hot gas from the compressor flows through the condenser, where it releases its heat to the surrounding air. The loss of heat causes the refrigerant to condense into a liquid.
The expansion valve is a small nozzle that controls the flow of the liquid refrigerant from the condenser to the evaporator. The expansion valve reduces the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, turning it into a cold liquid.
The evaporator is another coil of metal tubes that is located inside the refrigerator. The cold liquid from the expansion valve flows through the evaporator, where it absorbs the heat from the food and the air inside the refrigerator. The gain of heat causes the refrigerant to evaporate into a gas.
The gas then returns to the compressor, where the cycle is repeated. This is how a refrigerator works to keep the food and the air inside it cold.
Pertanyaan:
1. What is the main purpose of the text?
2. What is the name of the fluid that is used to transfer heat in a refrigerator?
3. What is the function of the compressor in a refrigerator?
4. What is the function of the condenser in a refrigerator?
5. What is the function of the expansion valve in a refrigerator?
6. What is the function of the evaporator in a refrigerator?
Jawaban:
1. The main purpose of the text is to explain how a refrigerator works.
2. The name of the fluid that is used to transfer heat in a refrigerator is a refrigerant.
3. The function of the compressor in a refrigerator is to compress the refrigerant and increase its pressure and temperature, turning it into a hot gas.
4. The function of the condenser in a refrigerator is to release the heat from the hot gas to the surrounding air and condense the refrigerant into a liquid.
5. The function of the expansion valve in a refrigerator is to control the flow of the liquid refrigerant and reduce its pressure and temperature, turning it into a cold liquid.
6. The function of the evaporator in a refrigerator is to absorb the heat from the food and the air inside the refrigerator and evaporate the refrigerant into a gas.
Soal 7
Bacalah teks berikut dengan seksama, kemudian jawablah pertanyaan yang ada di bawahnya.
Text 7
How Does a Solar Panel Work?
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity. Solar panels are made of many solar cells, which are the basic units of solar energy. A solar cell is a thin layer of silicon that has been treated with impurities to create a positive and a negative layer. The positive layer has fewer electrons than the negative layer, creating an electric field between them.
When sunlight hits the solar cell, some of the photons (particles of light) are absorbed by the silicon atoms, which then release some of their electrons. The electric field pushes these free electrons to the negative layer, creating a current of electricity. The more sunlight that hits the solar cell, the more electricity is generated.
The electricity from a single solar cell is very small, so many solar cells are connected together in a solar panel to produce more power. The electricity from a solar panel is direct current (DC), which means it flows in one direction. However, most appliances and devices use alternating current (AC), which means it changes direction periodically. Therefore, a device called an inverter is needed to convert the DC electricity from the solar panel into AC electricity that can be used by the grid or the household.
Pertanyaan:
1. What is the main purpose of the text?
2. What are the materials that make up a solar cell?
3. What is the role of the electric field in a solar cell?
4. What is the difference between DC and AC electricity?
5. What is the function of an inverter in a solar panel system?
Jawaban:
1. The main purpose of the text is to explain how a solar panel works.
2. The materials that make up a solar cell are silicon and impurities.
3. The role of the electric field in a solar cell is to push the free electrons to the negative layer, creating a current of electricity.
4. The difference between DC and AC electricity is that DC electricity flows in one direction, while AC electricity changes direction periodically.
5. The function of an inverter in a solar panel system is to convert the DC electricity from the solar panel into AC electricity that can be used by the grid or the household.
foto: freepik.com
Soal 8
Bacalah teks berikut dengan seksama, kemudian jawablah pertanyaan yang ada di bawahnya.
Text 8
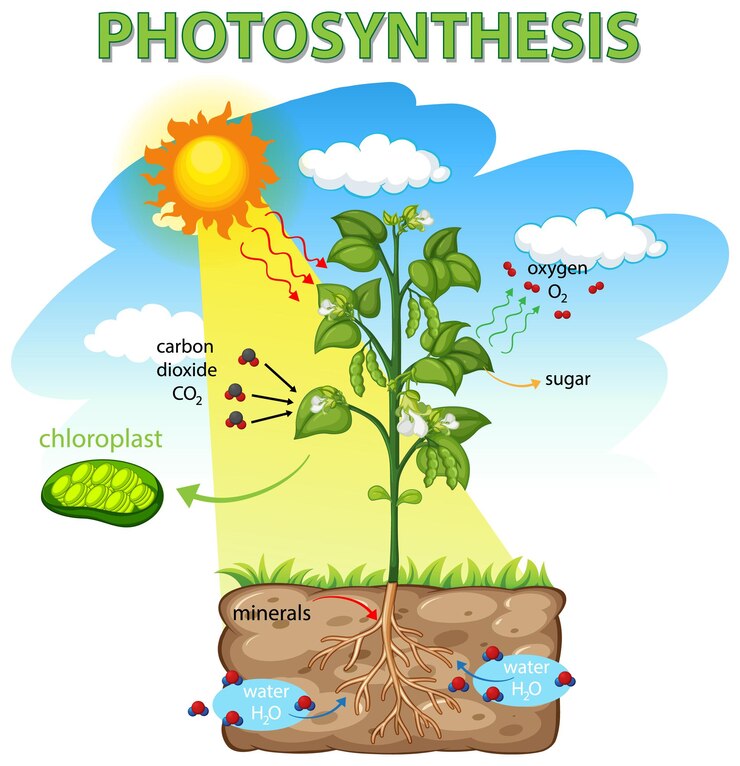
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria, allowing them to convert light energy into chemical energy. This process plays a crucial role in the Earth's ecosystem by producing oxygen and organic compounds, which serve as food for organisms higher up the food chain.
During photosynthesis, plants use chlorophyll, a green pigment found in chloroplasts, to capture light energy from the sun. This energy is used to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen ions, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. The hydrogen ions, along with carbon dioxide absorbed from the atmosphere, are then used to produce glucose through a series of chemical reactions known as the Calvin cycle.
The glucose produced during photosynthesis serves as the primary source of energy for plants and provides the building blocks for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and other essential molecules. Additionally, plants release oxygen into the atmosphere during photosynthesis, which is vital for the survival of aerobic organisms, including humans.
Photosynthesis is not only essential for the production of oxygen and food but also plays a significant role in regulating the Earth's climate. By absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, plants help mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing greenhouse gas levels.
Pertanyaan:
1. What is photosynthesis, and why is it important for plants?
2. How do plants capture light energy during photosynthesis?
3. What are the products of the light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis?
4. Explain the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis.
5. How is glucose produced during photosynthesis?
6. Why is oxygen released as a byproduct of photosynthesis?
7. What are the implications of photosynthesis for the Earth's ecosystem?
8. How does photosynthesis contribute to the regulation of the Earth's climate?
9. Discuss the significance of photosynthesis for human life.
Jawaban:
1. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, allowing them to produce glucose and oxygen, which are essential for their growth and survival.
2. Plants capture light energy using chlorophyll, a green pigment found in chloroplasts, which absorbs light in the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
3. The products of the light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis are oxygen, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
4. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy during photosynthesis and plays a crucial role in initiating the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
5. Glucose is produced during photosynthesis through the Calvin cycle, where carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions are used to synthesize glucose molecules.
6. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis during the light-dependent reactions when water molecules are split into oxygen and hydrogen ions.
7. Photosynthesis is essential for maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and providing food for organisms higher up the food chain.
8. Photosynthesis helps regulate the Earth's climate by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby reducing greenhouse gas levels and mitigating the effects of climate change.
9. Photosynthesis is crucial for human life as it produces oxygen for us to breathe and provides food in the form of fruits, vegetables, and grains. Additionally, photosynthesis plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance and sustaining biodiversity on Earth.
Soal 9
Bacalah teks berikut dengan seksama, kemudian jawablah pertanyaan yang ada di bawahnya.
Text 9
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics is a geological theory that explains the movement of Earth's lithosphere, which is divided into several large and small tectonic plates. These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them and interact with each other along their boundaries, leading to various geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formation.
The Earth's lithosphere is divided into approximately 20 major tectonic plates and several smaller ones. These plates are in constant motion, driven by the heat generated from the Earth's interior, convection currents in the mantle, and gravitational forces. There are three main types of plate boundaries: divergent boundaries, where plates move away from each other; convergent boundaries, where plates collide and subduction occurs; and transform boundaries, where plates slide past each other horizontally.
At divergent boundaries, such as mid-ocean ridges, new oceanic crust is formed as magma rises from the mantle and solidifies. This process, known as seafloor spreading, leads to the widening of ocean basins. Convergent boundaries are characterized by the collision of tectonic plates, resulting in the formation of mountain ranges, volcanic arcs, and deep ocean trenches. Subduction occurs when one plate is forced beneath another into the mantle, leading to the recycling of crustal material.
Transform boundaries, such as the San Andreas Fault in California, are associated with horizontal displacement along fault lines. Earthquakes often occur along these boundaries as the plates grind past each other. Plate tectonics not only shapes the Earth's surface but also influences the distribution of continents, the formation of ocean basins, and the evolution of life on our planet.
Understanding plate tectonics is essential for predicting geological hazards, such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and for exploring natural resources, including mineral deposits and fossil fuels. It provides valuable insights into the dynamic nature of Earth's geology and helps scientists unravel the mysteries of our planet's past, present, and future.
Pertanyaan:
1. What is plate tectonics, and how does it explain the movement of Earth's lithosphere?
2. Describe the three main types of plate boundaries and the geological features associated with each.
3. How does seafloor spreading occur at divergent boundaries?
4. What geological features are formed at convergent boundaries, and what processes drive their formation?
5. Explain the concept of subduction and its role in plate tectonics.
6. What geological phenomena are associated with transform boundaries?
7. How does plate tectonics influence the distribution of continents and the formation of ocean basins?
8. Why is understanding plate tectonics important for predicting geological hazards?
9. Discuss the significance of plate tectonics for Earth's geology and the exploration of natural resources.
Jawaban:
1. Plate tectonics is a geological theory that describes the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates, driven by convection currents in the mantle and gravitational forces.
2. The three main types of plate boundaries are divergent boundaries, where plates move apart; convergent boundaries, where plates collide; and transform boundaries, where plates slide past each other. Divergent boundaries are associated with mid-ocean ridges, convergent boundaries with mountain ranges and volcanic arcs, and transform boundaries with fault lines.
3. Seafloor spreading occurs at divergent boundaries when magma rises from the mantle and solidifies, forming new oceanic crust.
4. Convergent boundaries are associated with the formation of mountain ranges, volcanic arcs, and deep ocean trenches. Subduction occurs when one plate is forced beneath another into the mantle, leading to the recycling of crustal material.
5. Subduction is the process by which one tectonic plate is forced beneath another into the mantle at a convergent boundary.
6. Transform boundaries are associated with horizontal displacement along fault lines, resulting in earthquakes.
7. Plate tectonics influences the distribution of continents through the movement of tectonic plates and the formation of ocean basins through processes such as seafloor spreading and subduction.
8. Understanding plate tectonics is important for predicting geological hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis, which can have devastating effects on human populations and infrastructure.
9. Plate tectonics provides insights into Earth's geological processes and the distribution of natural resources such as mineral deposits, fossil fuels, and freshwater reserves. It also helps scientists reconstruct Earth's geological history and understand the forces shaping our planet's surface.
Recommended By Editor
- Kenapa bantalan rel kereta api selalu pakai batu kerikil?
- Masuk angin ternyata bukan penyakit, ini penjelasan ilmiahnya
- Kenapa Kucing Hilang Bisa Kembali Sendiri ke Rumah? Ini Penjelasannya
- Sering meniup makanan dan minuman panas ganggu kesehatan?
- Gorengan bisa bikin imun tubuh turun? Ini lho faktanya
- Benarkah air kelapa bisa mengatasi keracunan makanan? Simak faktanya
- Mitos atau fakta, makan ubi bisa bikin sering kentut?